코딩하는 해맑은 거북이
[데이터시각화] Bar Plot 본문
본 게시물의 내용은 '부스트캠프 AI Tech - Data Visualization(안수빈)' 강의를 듣고 작성하였다.
해당 글은 아래의 7가지를 다룬다.
🍀 Bar plot 이란?
🍀 Bar Plot의 종류 4가지
🚩 Student Score Dataset
📊 Multiple Bar Plot
📊 Stacked Bar Plot
📊 Overlapped Bar Plot
📊 Grouped Bar Plot
🍀 Bar Plot의 원칙
🍀 데이터 정렬
🍀 적절한 공간 활용
🍀 복잡함과 단순함
🍀 오차막대 (errorbar)
- Bar plot이란 직사각형 막대를 사용하여 데이터의 값을 표현하는 차트/그래프
- 막대 그래프, bar chart, bar graph 등의 이름으로 사용됨
- 범주(category)에 따른 수치 값을 비교하기에 적합한 방법
→ 개별 비교, 그룹 비교 모두 적합
- 막대의 방향에 따른 분류 (.bar() / .barh())
- 수직 (vertical) : x축에 범주, y축에 값을 표기. (default)
- 수평 (horizontal) : y축에 범주, x축에 값을 표기. (범주가 많을 때 적합하다)
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 7))
x = list('ABCDE')
y = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
axes[0].bar(x, y)
axes[1].barh(x, y)
plt.show()
- 막대그래프 색 변경 : 전체:color='색' / 개별:color='컬러리스트'
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 7))
x = list('ABCDE')
y = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
clist = ['blue', 'gray', 'gray', 'gray', 'red']
color = 'green'
axes[0].bar(x, y, color=clist)
axes[1].barh(x, y, color=color)
plt.show()
🚩 앞서 데이터셋 준비! Student Score Dataset 으로 시각화해보기.
- 1000명 학생 데이터
- feature에 대한 정보는 head(), describe(), info() 등으로 확인하고
- unique(), value_counts() 등으로 종류나 큰 분포 확인
- features
- 성별 : female / male
- 인종민족 : group A, B, C, D, E
- 부모님 최종 학력 : 고등학교 졸업, 전문대, 학사 학위, 석사 학위, 2년제 졸업
- 점심 : standard와 free/reduced
- 시험 예습 : none과 completed
- 수학, 읽기, 쓰기 성적 (0~100)
student = pd.read_csv('./StudentsPerformance.csv')
student.sample(5) # sample(5) : 랜덤하게 5개를 뽑아줌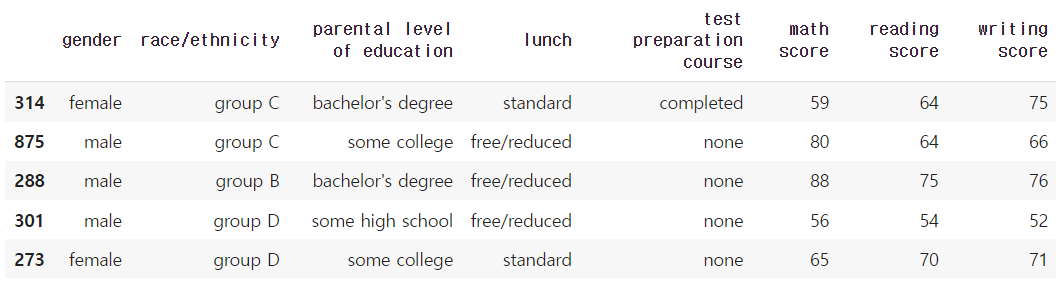
student.info() # 데이터 타입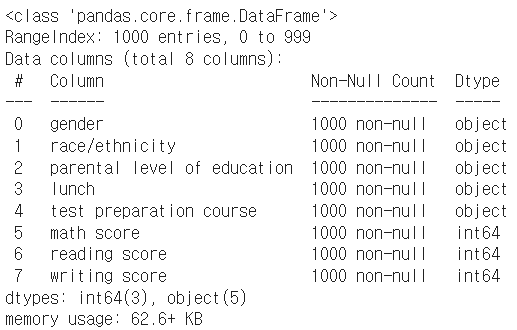
student.describe(include='all') # 통계정보 확인하기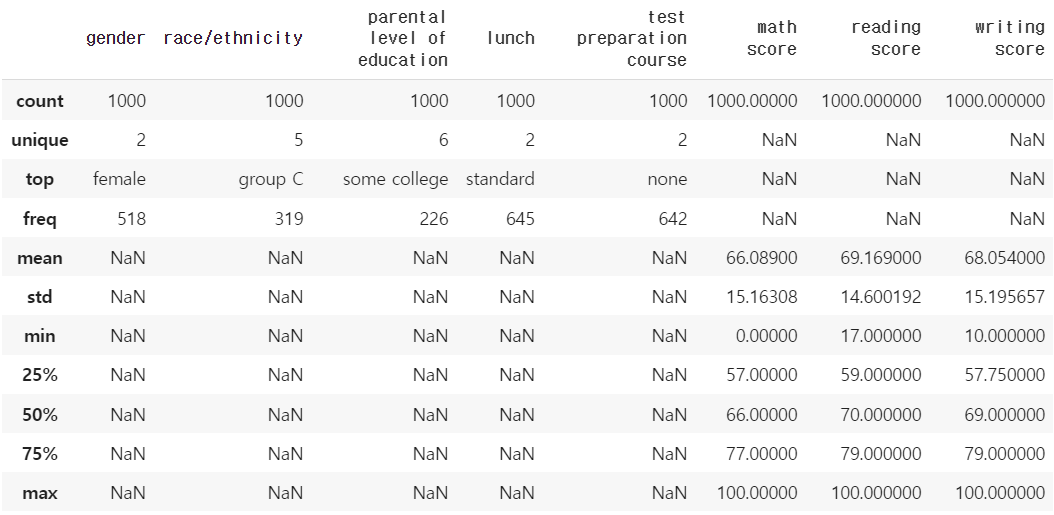
성별에 따른 race/ethincity 분포를 시각화 해보자.
group = student.groupby('gender')['race/ethnicity'].value_counts().sort_index()
display(group)
print(student['gender'].value_counts())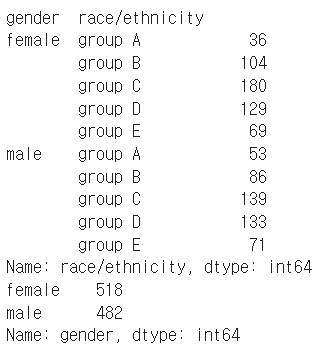
📊 Multiple Bar Plot : 플롯을 여러 개 그리는 방법
* male, female로 플롯을 2개 생성
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 7))
axes[0].bar(group['male'].index, group['male'], color='royalblue')
axes[1].bar(group['female'].index, group['female'], color='tomato')
plt.show()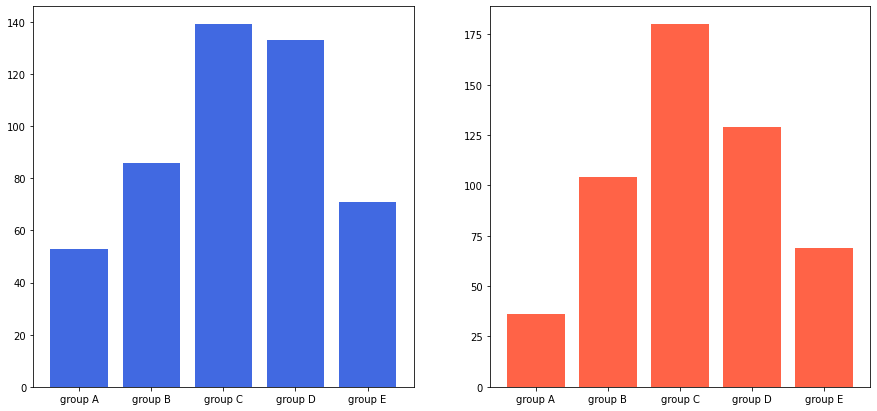
위 그림에서 두개의 플롯이 y축이 달라서 비슷하게 보인다.
아래와 같이 y축 값을 동일하게 해주어야 명확하게 차이가 보일 것이다.
* y축을 공유하는 방법 1 : plt.subplots(... , sharey=True)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 7), sharey=True)
axes[0].bar(group['male'].index, group['male'], color='royalblue')
axes[1].bar(group['female'].index, group['female'], color='tomato')
plt.show()
* y축을 공유하는 방법 2 : 반복문으로 y축의 범위를 개별적으로 설정
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 7))
axes[0].bar(group['male'].index, group['male'], color='royalblue')
axes[1].bar(group['female'].index, group['female'], color='tomato')
for ax in axes:
ax.set_ylim(0, 200)
plt.show()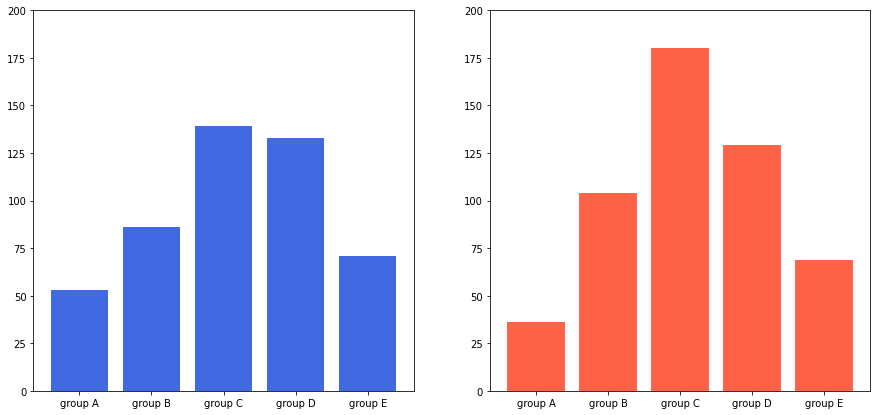
📊 Stacked Bar Plot : 한 개의 플롯에 동시에 나타내는 방법(쌓아서 표현하는 방법)
- 2개 이상의 그룹을 쌓아서(stack) 표현하는 bar plot
- 각 bar에서 나타나는 그룹의 순서는 항상 유지
- 맨 밑의 bar의 분포는 파악하기 쉽지만 그 외의 분포들은 파악하기 어렵다는 단점이 있다
- 2개의 그룹이 positive/negative라면 축 조정 가능
- .bar()에서는 bottom 파라미터를 사용
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 7))
group_cnt = student['race/ethnicity'].value_counts().sort_index()
axes[0].bar(group_cnt.index, group_cnt, color='darkgray')
axes[1].bar(group['male'].index, group['male'], color='royalblue')
axes[1].bar(group['female'].index, group['female'], bottom=group['male'], color='tomato')
for ax in axes:
ax.set_ylim(0, 350)
plt.show()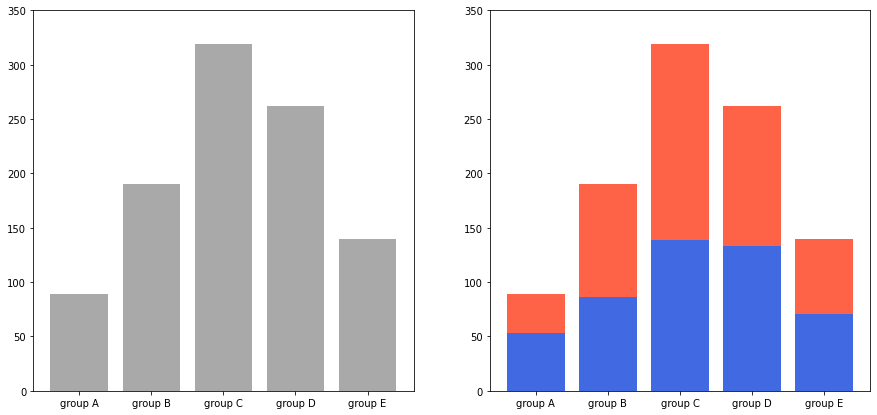
- .barh()에서는 left 파라미터를 사용
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 7))
group_cnt = student['race/ethnicity'].value_counts().sort_index()
axes[0].barh(group_cnt.index, group_cnt, color='darkgray')
axes[1].barh(group['male'].index, group['male'], color='royalblue')
axes[1].barh(group['female'].index, group['female'], left=group['male'], color='tomato')
for ax in axes:
ax.set_xlim(0, 350)
plt.show()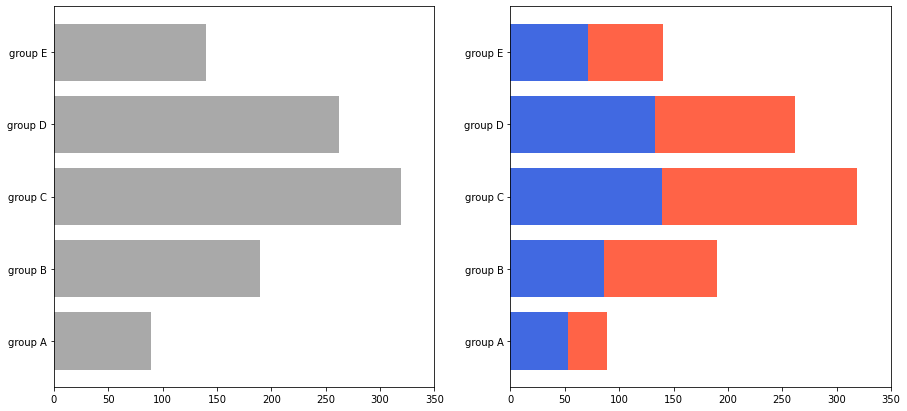
- 응용하여 전체에서 비율을 나타내는 Percentage Stacked Bar Chart가 있음
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 7))
group = group.sort_index(ascending=False) # 역순 정렬
total=group['male']+group['female'] # 각 그룹별 합
ax.barh(group['male'].index, group['male']/total, color='royalblue')
ax.barh(group['female'].index, group['female']/total,
left=group['male']/total, color='tomato')
ax.set_xlim(0, 1) # 범위를 주어 오른쪽 여백 제거
for s in ['top', 'bottom', 'left', 'right']:
ax.spines[s].set_visible(False) # 테두리 없애기
plt.show()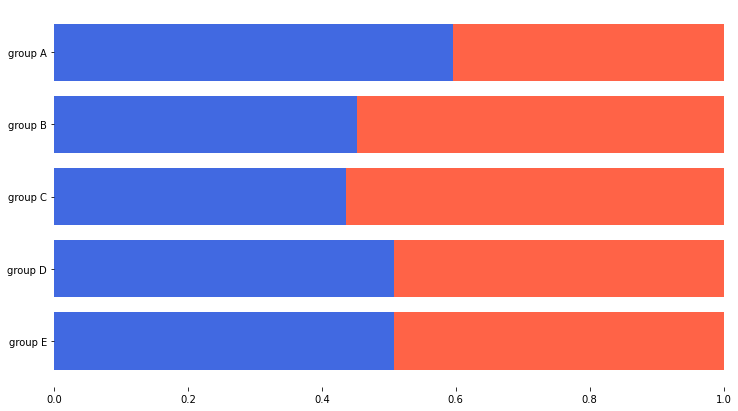
📊 Overlapped Bar Plot : 한 개의 플롯에 동시에 나타내는 방법(겹쳐서 표현하는 방법)
- 2개 그룹만 비교한다면 겹쳐서 만드는 것도 하나의 선택지이다
→ 3개 이상에서는 파악이 어렵다는 단점이 있다
- 같은 축을 사용하니 비교가 쉬움
→ 투명도를 조정하여 겹치는 부부 파악 (alpha)
- Bar plot보다는 Area plot에서 더 효과적
* alpha = 1, 0.7, 0.5, 0.3 에 따른 플롯비교, alpha가 0에 가까울수록 투명도가 높다.
group = group.sort_index() # 다시 정렬
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 12))
axes = axes.flatten()
for idx, alpha in enumerate([1, 0.7, 0.5, 0.3]):
axes[idx].bar(group['male'].index, group['male'],
color='royalblue',
alpha=alpha)
axes[idx].bar(group['female'].index, group['female'],
color='tomato',
alpha=alpha)
axes[idx].set_title(f'Alpha = {alpha}')
for ax in axes:
ax.set_ylim(0, 200)
plt.show()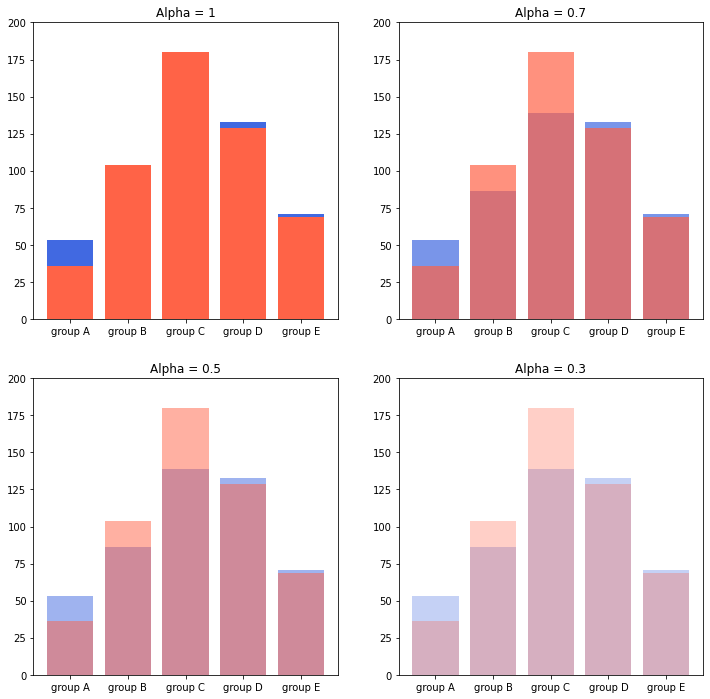
📊 Grouped Bar Plot : 한 개의 플롯에 동시에 나타내는 방법(이웃에 배치하여 표현하는 방법)
- 그룹별 범주에 따른 bar를 이웃되게 배치하는 방법
- Matplotlib으로는 비교적 구현이 까다롭다는 단점이 있다
→ 적당한 테크닉 (.set_xticks(), .set_xticklabels())
- 앞서 소개한 내용 모두 그룹이 5개~7개 이하일 때 효과적 / 그 이상이면 그룹보다 범주간의 비교가 되기때문
→ 그룹이 많다면 적은 그룹은 ETC로 처리
- 크게 3개의 테크닉으로 구현 가능하다.
- x축 조정
- width 조정
- xticks, xticklabels
*그룹이 2개일 때, 원래 x축이 0, 1, 2, 3로 시작한다면 (중심점 설정)
- 한 그래프는 0-width/2, 1-width/2, 2-width/2 로 구성
- 다른 한 그래프는 0+width/2, 1+width/2, 2+width/2 로 구성
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 7))
idx = np.arange(len(group['male'].index))
width=0.35
ax.bar(idx-width/2, group['male'],
color='royalblue',
width=width, label='Male')
ax.bar(idx+width/2, group['female'],
color='tomato',
width=width, label='Female')
ax.set_xticks(idx)
ax.set_xticklabels(group['male'].index)
ax.legend()
plt.show()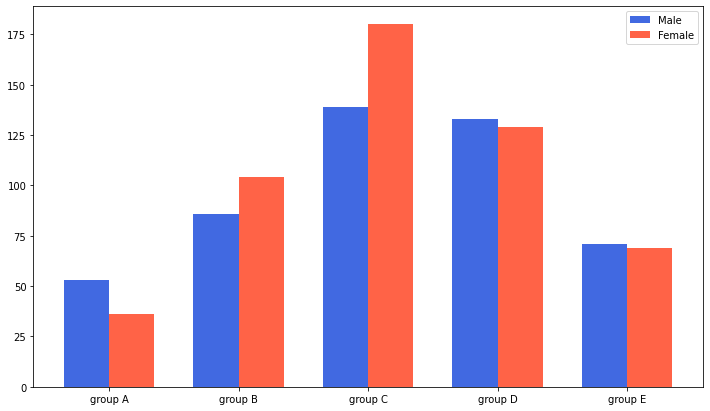
* 그룹이 N개 일때는?
그룹의 갯수에 따른 x좌표는 다음과 같다.
- 2개 : -1/2, +1/2
- 3개 : -1, 0, +1 (-2/2, 0, +2/2)
- 4개 : -3/2, -1/2, +1/2, +3/2
이와 같이 -(N-1)/2 ~ (N-1)/2 까지 분자에 2간격으로 커진다.
index i (zero-index)에 대해서는 x좌표를 아래의 식으로 계산해준다.
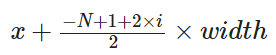
Sgroup = student.groupby('parental level of education')['race/ethnicity'].value_counts().sort_index()
group_list = sorted(student['race/ethnicity'].unique())
edu_lv = student['parental level of education'].unique()fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(13, 7))
x = np.arange(len(group_list))
width=0.12
for idx, g in enumerate(edu_lv):
ax.bar(x+(-len(edu_lv)+1+2*idx)*width/2, group[g],
width=width, label=g)
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(group_list)
ax.legend()
plt.show()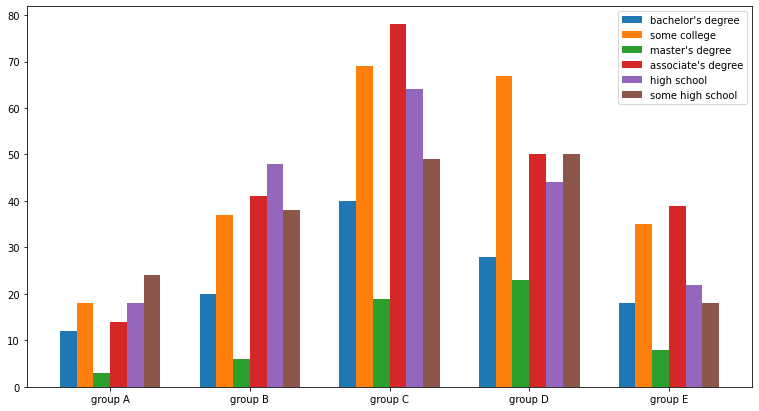
The representation of numbers, as physically measured on the surface of the graphic itself, should be directly proportional to the numerical quantities represented.
- 실제 값과 그에 표현되는 그래픽으로 표현되는 잉크 양은 비례해야 함
- 반드시 x축의 시작은 zero(0)!!
- 막대 그래프에만 한정되는 원칙은 아니다!
→ Area plot, Donut Chart 등등 다수의 시각화에서 적용됨
- (아래 예제) 인지의 방해를 주지 않고 싶다면
→ 축을 x축으로 시작은 0으로 설정하거나
→ 만약 차이를 나타내고 싶다면 plot의 세로 비율을 늘려준다.
성별에 따른 성적을 막대그래프로 시각화
score = student.groupby('gender').mean().T
score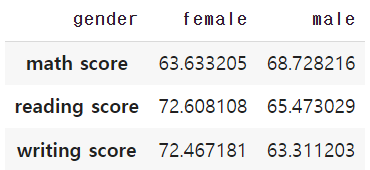
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 7))
idx = np.arange(len(score.index))
width=0.3
for ax in axes:
ax.bar(idx-width/2, score['male'],
color='royalblue',
width=width)
ax.bar(idx+width/2, score['female'],
color='tomato',
width=width)
ax.set_xticks(idx)
ax.set_xticklabels(score.index)
axes[0].set_ylim(60, 75)
plt.show()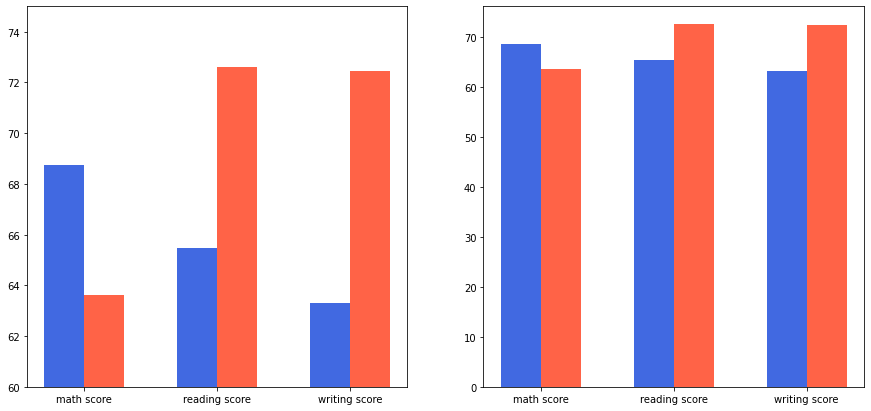
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6, 10))
idx = np.arange(len(score.index))
width=0.3
ax.bar(idx-width/2, score['male'],
color='royalblue',
width=width)
ax.bar(idx+width/2, score['female'],
color='tomato',
width=width)
ax.set_xticks(idx)
ax.set_xticklabels(score.index)
plt.show()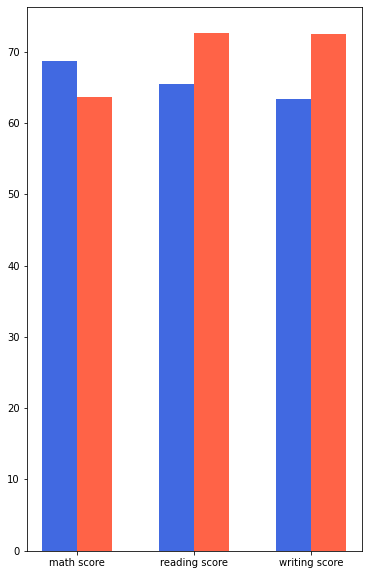
- 더 정확한 정보를 전달하기 위해서는 정렬이 필수
→ Pandas에서는 sort_values(), sort_index()를 사용하여 정렬
- 데이터의 종류에 따라 다음 기준으로
- 시계열 | 시간순
- 수치형 | 크기순
- 순서형 | 범주의 순서대로
- 명목형 | 범주의 값 따라 정렬
- 여러 가지 기준으로 정렬을 하여 패턴을 발견
- 대시보드에서는 Interactive로 제공하는 것이 유용
- 여백과 공간만 조정해도 가독성이 높아진다.
- Matplotlib의 bar plot은 ax에 꽉 차서 살짝 답답함
- Matplotlib techniques
- X/Y axis Limit (.set_xlim(), .set_ylime())
- Spines (.spines[spine].set_visible())
- Gap (width)
- Legend (.legend())
- Margins (.margins())
group_cnt = student['race/ethnicity'].value_counts().sort_index()
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 7))
ax_basic = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax_basic.bar(group_cnt.index, group_cnt)
ax.bar(group_cnt.index, group_cnt,
width=0.7, # 막대그래프 두께
edgecolor='black', # 테두리
linewidth=2, # 테두리 두께
color='royalblue'
)
ax.margins(0.1, 0.1) # 전체 테두리쪽 여백 늘리기 (default:5%)
for s in ['top', 'right']:
ax.spines[s].set_visible(False) # 오른쪽, 위쪽 테두리 제거
plt.show()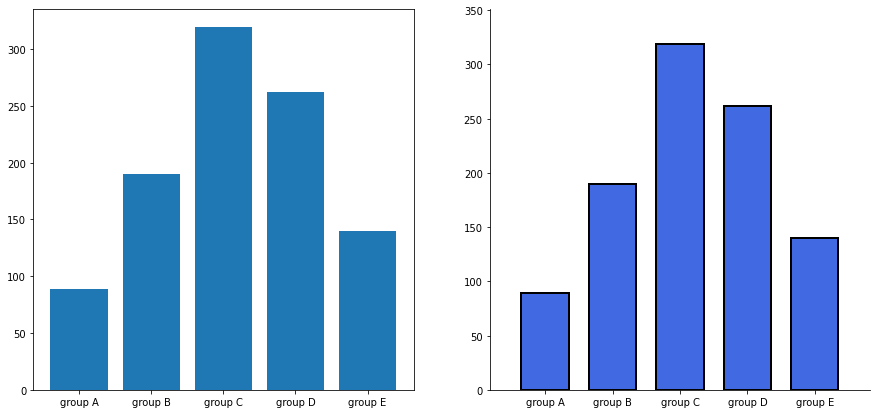
- 필요 없는 복잡함은 NO!!! 무의미한 3D는 Never…
→ 직사각형이 아닌 다른 형태의 bar는 지양
- 무엇을 보고 싶은가? (시각화를 보는 대상이 누구인가?)
→ 정확한 차이 (EDA)
→ 큰 틀에서 비교 및 추세 파악 (Dashboard)
- 축과 디테일 등의 복잡함
- Grid (.grid())
- Ticklabels (.set_ticklabels())
- Major & Minor
- Text를 어디에 어떻게 추가할 것인가 (.text() or .annotate())
- Bar의 middle / upper
group_cnt = student['race/ethnicity'].value_counts().sort_index()
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 7))
for ax in axes:
ax.bar(group_cnt.index, group_cnt,
width=0.7,
edgecolor='black',
linewidth=2,
color='royalblue',
zorder=10
)
ax.margins(0.1, 0.1)
for s in ['top', 'right']:
ax.spines[s].set_visible(False)
axes[1].grid(zorder=0) # 그리드 추가
for idx, value in zip(group_cnt.index, group_cnt):
axes[1].text(idx, value+5, s=value, # 텍스트 추가
ha='center',
fontweight='bold'
)
plt.show()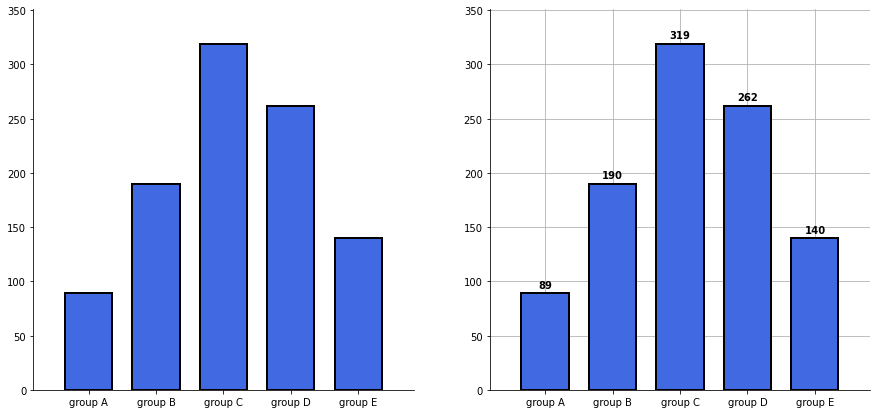
- 오차 막대를 추가하여 Uncertainty 정보를 추가 가능 (errorbar)
- Bar 사이 Gap이 0이라면 -> 히스토그램(Histogram)
- .hist()를 사용하여 가능
- 연속된 느낌을 줄 수 있음
- 다양한 Text 정보 활용하기
- 제목 (.set_title())
- 라벨 (.set_xlabel(), .set_ylabel())
오차막대(errorbar)를 사용하여 편차 등의 정보를 추가
score_var = student.groupby('gender').std().T
score_var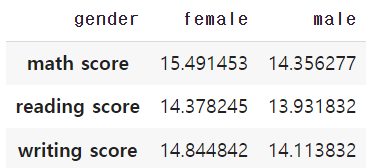
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 10))
idx = np.arange(len(score.index))
width=0.3
ax.bar(idx-width/2, score['male'],
color='royalblue',
width=width,
label='Male',
yerr=score_var['male'],
capsize=10 # 위쪽, 아래쪽에 에러에 대한 범위를 잡아줌
)
ax.bar(idx+width/2, score['female'],
color='tomato',
width=width,
label='Female',
yerr=score_var['female'],
capsize=10
)
ax.set_xticks(idx)
ax.set_xticklabels(score.index)
ax.set_ylim(0, 100)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.legend()
ax.set_title('Gender / Score', fontsize=20)
ax.set_xlabel('Subject', fontweight='bold') # x축 라벨
ax.set_ylabel('Score', fontweight='bold') # y축 라벨
plt.show()
'Data Analysis & Viz' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [데이터시각화] Text (0) | 2023.03.22 |
|---|---|
| [데이터시각화] Scatter Plot (0) | 2023.03.22 |
| [데이터시각화] Line Plot (0) | 2023.03.22 |
| [데이터시각화] Matplotlib (0) | 2023.03.21 |
| [데이터시각화] 시각화의 요소 (0) | 2023.03.21 |




