코딩하는 해맑은 거북이
[자료구조] 트리(Tree), 이진트리, 이진트리 순회, 이진탐색트리(BST) 본문
트리
- 계층적인 구조
- 사이클을 포함하지 않음 (부모-자식 관계)
- 특별 노드(root)가 존재
- 서로 독립적인 서브트리를 가짐
트리의 종류
- 일반 트리 : 자식 노드의 수가 제한이 없음
- 이진 트리 : 자식 노드의 수가 2개 이하이다.
트리 기초 용어
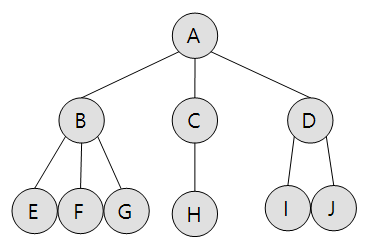
- 루트(root) : 최상위 노드 (ex) A
- 단말노드(terminal node) : 자식이 없는 노드 (ex) E,F,G,H,I,J
- 형제노드(sibling) : 같은 층에 있는 노드 (ex) E,F,G
- 레벨(level) : 트리의 각층의 번호
- 높이(height) : 트리의 최대 레벨 (ex) 3
- 차수(degree) : 노드가 가지고 있는 자식 노드의 개수 (ex) B의 차수는 3
트리의 표현
- 일반적인 구조 → 문제점 : 노드의 차수에 따라 link가 가변적이다.

- 이진트리의 구조 → 고정된 공간만 사용하며 프로그램이 간단해진다.
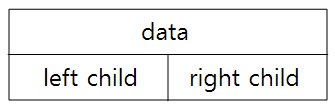
이진트리
- 이진트리의 정의
2개 이하의 서브트리(왼쪽 혹은 오른쪽 서브트리)로 구성되며, 서브트리 간의 순서가 존재한다.
- 이진트리의 종류
1) 경사이진트리 (skewed binary tree)

2) 완전이진트리 (complete binary tree)
3) 포화이진트리 (full binary tree)
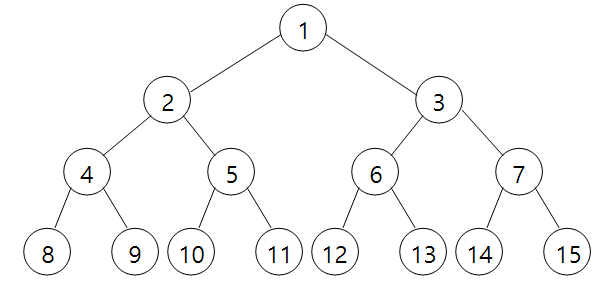
이진트리 : 배열 표현
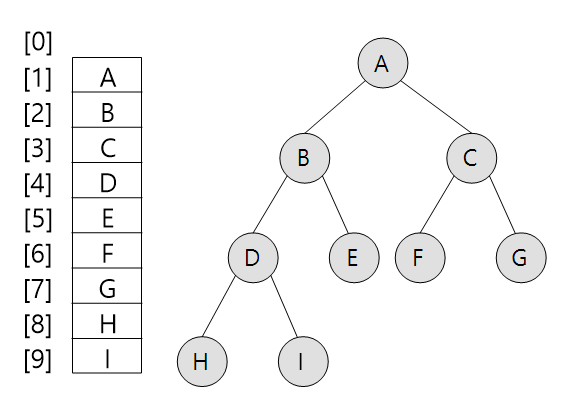
* 이진트리의 특성 (n : 노드의 갯수)
- 노드 i의 부모 : i/2 (if i ≠ 1)
- 노드 i의 왼쪽 자식 : 2i (if 2i ≤ n)
- 노드 i의 오른쪽 자식 : 2i+1 (if 2i+1 ≤ n)
* 이진트리 성질
- 레벨 i에서 노드 수 : \(2^i-1\)개
- 높이가 h일 경우 최대 노드 수 : \(2^h-1\)개
- 높이가 h일 경우 최소 노드 수 : h개
- n개의 노드를 갖는 이진트리의 높이 : \(log_2(n+1)\)
이진트리 : 연결리스트 표현
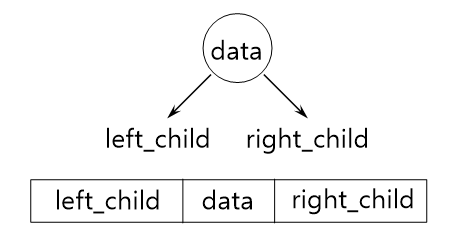
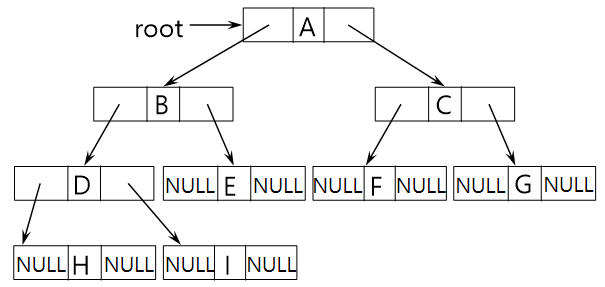
* 구조체 정의
typedef struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left;
struct Node *right;
}Node;
이진트리 순회
- 순회 : 트리의 노드들을 방문하여 방문한 노드들을 차례로 출력
- 순회방법 ( L : Left, V : Visit, R : Right )
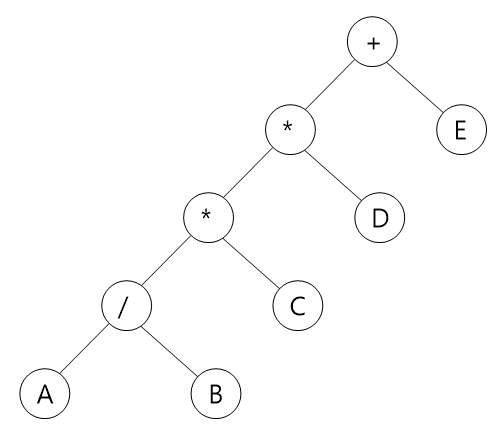
1) 전위순회(preorder traversal) : VLR - Stack 사용(순환함수)
결과 : +**/ABCDE
void Preorder(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
printf("%c", root->data);
Preorder(root->left);
Preorder(root->right);
}
2) 중위순회(inorder traversal) : LVR - Stack 사용(순환함수)
결과 : A/B*C*D+E
void Inorder(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
Inorder(root->left);
printf("%c", root->data);
Inorder(root->right);
}
3) 후위순회(postorder traversal) : LRV - Stack 사용(순환함수)
결과 : AB/C*D*E+
void Postorder(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
Postorder(root->left);
Postorder(root->right);
printf("%c", root->data);
}
4) 레벨순회(Level order traversal) - Queue 사용
결과 : +*E*D/CAB
void Levelorder(Node* ptr)
{
if (!ptr)
return;
enqueue(ptr);
while (!is_empty()) {
ptr = dequeue();
printf("%c", ptr->data);
if (ptr->left)
enqueue(ptr->left);
if (ptr->right)
enqueue(ptr->right);
}
}
* 시간복잡도 : O(n), (n : 노드의 갯수)
* 공간복잡도 : O(h), (h : 트리의 높이)
cf) h : 경사트리일 때 n, 완전이진트리일 때 \(log_2(n+1)\) 이다.
- 이진 트리 높이 계산
결과 : 5
#ifndef max
#define max(a,b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#endif
int get_height(Node* node)
{
int height = 0;
if (node != NULL)
height = 1 + max(get_height(node->left), get_height(node->right));
return height;
}
전체 소스코드
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 10
typedef struct Node
{
char data;
struct Node *left;
struct Node *right;
}Node;
typedef Node* element;
element queue[MAX_SIZE];
int rear = -1;
int front = -1;
int is_empty()
{
return (front == rear);
}
int is_full()
{
return (front == (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE);
}
void enqueue(element item)
{
if (is_full()) {
return;
}
else {
rear = (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
queue[rear] = item;
}
}
element dequeue()
{
if (is_empty()) {
return 0;
}
else {
front = (front + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
return queue[front];
}
}
void Preorder(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
printf("%c", root->data);
Preorder(root->left);
Preorder(root->right);
}
void Inorder(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
Inorder(root->left);
printf("%c", root->data);
Inorder(root->right);
}
void Postorder(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
Postorder(root->left);
Postorder(root->right);
printf("%c", root->data);
}
void Levelorder(Node* ptr)
{
if (!ptr)
return;
enqueue(ptr);
while (!is_empty()) {
ptr = dequeue();
printf("%c", ptr->data);
if (ptr->left)
enqueue(ptr->left);
if (ptr->right)
enqueue(ptr->right);
}
}
#ifndef max
#define max(a,b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
#endif
int get_height(Node* node)
{
int height = 0;
if (node != NULL)
height = 1 + max(get_height(node->left), get_height(node->right));
return height;
}
void main()
{
Node n1 = { 'A', NULL, NULL};
Node n2 = { 'B', NULL, NULL };
Node n3 = { '/', &n1, &n2 };
Node n4 = { 'C', NULL, NULL };
Node n5 = { '*', &n3, &n4 };
Node n6 = { 'D', NULL, NULL };
Node n7 = { '*', &n5, &n6 };
Node n8 = { 'E', NULL, NULL };
Node n9 = { '+', &n7, &n8 };
Node* root = &n9;
Preorder(root);//VLR
printf("\n");
Inorder(root);//LVR
printf("\n");
Postorder(root);//LRV
printf("\n");
Levelorder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("%d\n", get_height(root));
}
응용
이진탐색트리(Binary Search Tree : BST)
- 정의
(1) 모든 노드는 유일한 키 값을 가진다.
(2) 왼쪽 서브트리의 키 값 ≤ 한 노드의 키 값 ≤ 오른쪽 서브트리의 키 값
(3) 모든 노드에서 위 두 특성을 유지한다.
- 특징
탐색, 삽입, 삭제 연산 : O(h) (h : 트리의 높이)
이진탐색트리를 중위순회(Inorder traversal)하면 오름차순으로 정렬된 순서로 출력된다.
- 탐색 연산

root 노드에서부터 비교해서
* 해당 노드의 키 값보다 탐색할 키 값이 작으면 왼쪽 노드
* 해당 노드의 키 값보다 탐색할 키 값이 크면 오른쪽 노드로 이동해서 탐색 과정을 반복한다.
반복 과정에서 탐색할 키 값을 찾으면 이를 반환하고, NULL이 나온다면 해당 트리에 탐색할 키가 없는 것이다.
int Search(Tree *tree, int data, Node **parent)
{
Node *cur = tree->root;
while (true)
{
if (cur->key == data) // 탐색할 키 값을 찾음
return 1;
else if (cur->key > data) // 왼쪽 노드 탐색
{
*parent = cur;
if (cur->left == NULL)
return 0;
cur = cur->left;
}
else // 오른쪽 노드 탐색
{
*parent = cur;
if (cur->right == NULL)
return 0;
cur = cur->right;
}
}
}
- 삽입 연산
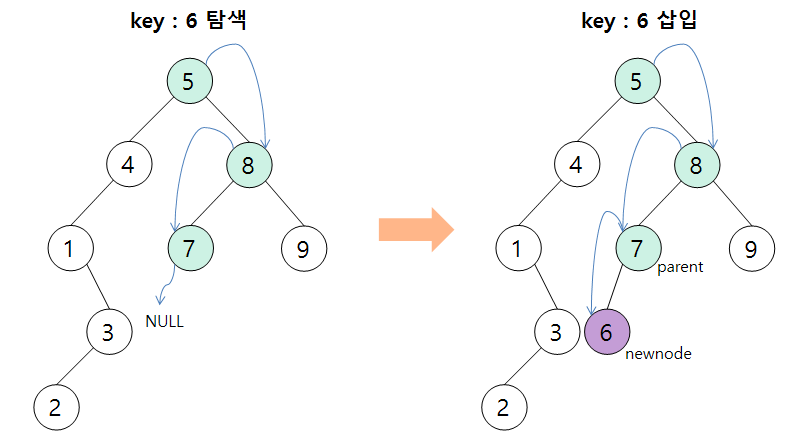
삽입할 키 값을 먼저 탐색 연산을 통해 트리에 존재하는지 확인한다.
없다면 parent 노드의 키 값과 비교하여 작으면 왼쪽 노드, 크면 오른쪽 노드에 newnode를 삽입한다.
void Insert(Tree *tree, int data)
{
Node *newnode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node *parent = NULL;
newnode->key = data;
newnode->left = NULL;
newnode->right = NULL;
if (tree->root == NULL)
{
tree->root = newnode;
return;
}
if (Search(tree, data, &parent))
{
return;
}
else
{
if (parent->key > data)
{
parent->left = newnode;
return;
}
else
{
parent->right = newnode;
return;
}
}
}
- 삭제 연산
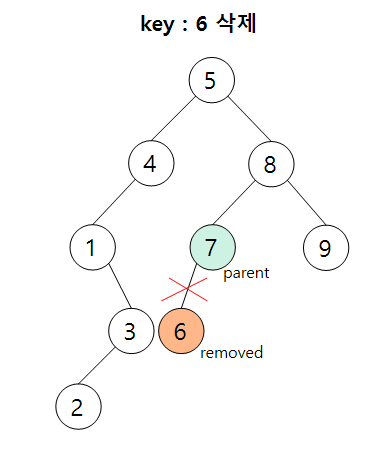
1) Case 1 : 삭제 노드가 단말 노드일 때
삭제 노드의 parent 연결 링크를 NULL로 초기화시켜준다.
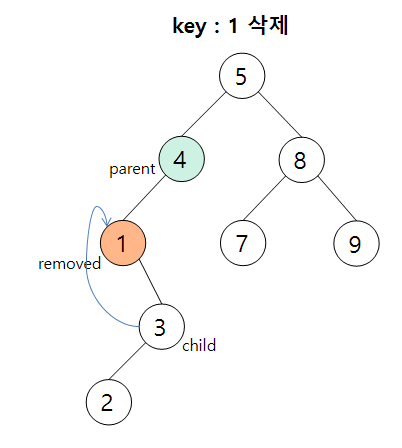
2) Case 2 : 삭제 노드가 한 개의 자식만을 가질 때
삭제 노드의 child 노드를 parent 링크에 연결시켜준다.
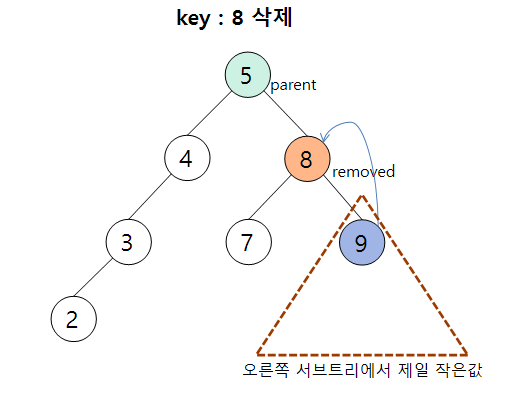
3) Case 3 : 삭제 노드가 두 개의 자식을 가질 때
삭제하는 방법 2가지는
- 왼쪽 서브트리에서 제일 큰 값
- 오른쪽 서브트리에서 제일 작은 값
을 삭제 노드에 이동시켜준다. 여기서는 오른쪽 서브트리에서 제일 작은 값을 선택하는 방법을 택했다.
void Delete(Tree *tree, int data)
{
Node *current = tree->root;
Node *parent = NULL;
Node *child = NULL;
Node *temp = NULL;
Node *tempCurrent = NULL;
if (!Search(tree, data, &parent))
return;
while (current->key != data)
{
if (current->key < data)
{
parent = current;
current = current->right;
}
else
{
parent = current;
current = current->left;
}
}
// case 1 : 삭제 노드가 단말 노드일 때
if (current->left == NULL && current->right == NULL)
{
if (parent->left == current)
parent->left = NULL;
else
parent->right = NULL;
free(current);
}
// Case 2 : 삭제 노드가 한 개의 자식만을 가질 때
else if (current->left == NULL || current->right == NULL)
{
if (current->left != NULL)
child = current->left;
else
child = current->right;
if (parent->left == current)
parent->left = child;
else
parent->right = child;
free(current);
}
// Case 3 : 삭제 노드가 두 개의 자식을 가질 때
else
{
tempCurrent = current;
temp = current->right;
while (temp->left != NULL)
{
tempCurrent = temp;
temp = temp->left;
}
if (tempCurrent->left == temp)
tempCurrent->left = temp->right;
else
tempCurrent->right = temp->right;
current->key = temp->key;
free(temp);
}
}
* n개의 원소를 갖는 이진탐색트리의 (탐색, 삽입, 삭제)의 시간복잡도
Average Case : O(log_2n) ← 완전 이진트리
Worst Case : O(n) ← 경사 이진트리
'Data Structure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] 정렬(Sort) (0) | 2023.02.05 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] 큐(Queue), 원형 큐, 회문 판정 (0) | 2023.02.03 |
| [자료구조] 스택(Stack), 괄호검사, 후위식 계산, 중위식의 후위식 변환 (0) | 2023.02.03 |
| [자료구조] 연결리스트(Linked List) (0) | 2023.02.03 |
| [자료구조] 배열 및 구조체, 다항식 덧셈, 희소행렬 전치 (0) | 2023.02.03 |




